Overview
Laboratory Introduction
Artificial Intelligence Digital Twin Lab (AIDTL)
Artificial Intelligence Digital Twin Lab (AIDTL)
Related Researcher

Jin Mo Goo Professor
- Email : jmgoo@snu.ac.kr
Research topics
Research goals
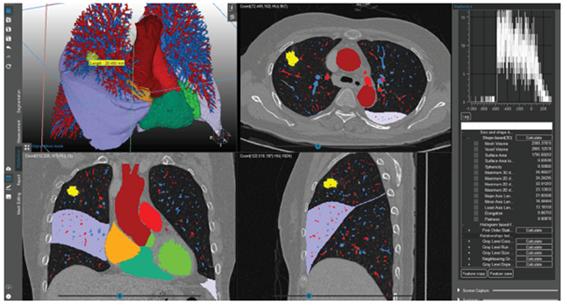
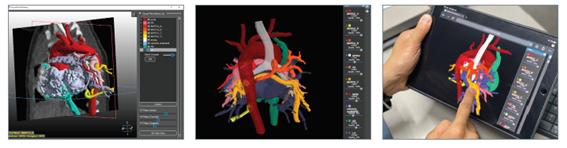
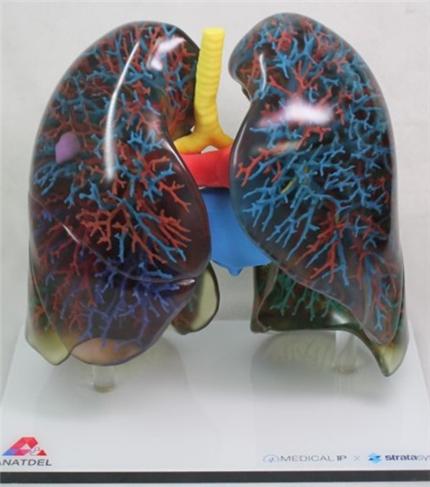
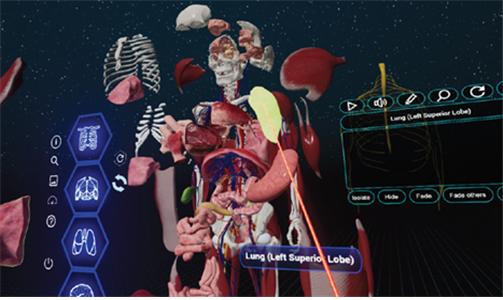
Research achievements
Automated Lung Segmentation on Chest Computed Tomography Images with Extensive Lung Parenchymal Abnormalities Using a Deep Neural Network. Korean J Radiol. 2020;21:e163. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0318.2020-10-01 PMID: 33169549
Differentiation of left atrial appendage thrombus from circulatory stasis using cardiac CT radiomics in patients with valvular heart disease. Eur Radiol, Cardiac, Published: 19 August 20202020-08-19 PMID : 32812175
Anterior Pulmonary Ventilation Abnormalities in COVID-19. Radiology. 2020 Nov;297(2):E276-E277. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020203043. Epub 2020 Aug 13.2020-08-13 PMID: 32787702
Prognostic Implication of Volumetric Quantitative CT Analysis in Patients with COVID-19: A Multicenter Study in Daegu, Korea. Korean J Radiol. 2020;21:e130. English. Published online Aug 04, 2020.2020-08-04 PMID: 32767868
Extension of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) on Chest CT and Implications for Chest Radiograph Interpretation. Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging. Vol. 2, No. 2 (Mar 30 2020)2020-03-30
Application of computerized 3D-CT texture analysis of pancreas for the assessment of patients with diabetes. PLoS One. 2020 Jan 13;15(1):e0227492. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227492. eCollection 2020.2020-01-13P MID: 31929591
Advanced Medical Use of Three-Dimensional Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease: Augmented Reality, Mixed Reality, Virtual Reality, and Three-Dimensional Printing. Korean J Radiol. 2020;21:e6. English. Published online Jan 08, 2020.2020-01-08 PMID: 31997589
Relationships between Spinal Sarcopenia and Spinal Sagittal Balance in Older Women. Annals of Geriatric Medicine and Research . 2019 Sep;23(3):141-148. doi: 10.4235/agmr.19.0030. Epub 2019 Sep 25.2019-09-25 PMID : 32743302